COOH-MSNs微球:精准药物递送的下一代解决方案
—— CDMO 服务赋能从实验室到临床的快速转化
在全球医药创新不断加速的背景下,药物递送系统已成为推动精准医疗的重要引擎。如何在保证药效的同时,降低毒副作用、提升靶向性与患者依从性,是制药企业与科研机构共同关注的核心问题。
COOH-MSNs Microspheres(羧基功能化介孔二氧化硅纳米球) 作为一种新型纳米载体材料,凭借其可控的结构、丰富的表面化学修饰能力与优异的生物相容性,正逐步走向临床转化与产业化。
作为专业 CDMO服务商,中新康明为合作伙伴提供从处方开发到 GMP 级生产的一体化服务,助力 COOH-MSNs微球技术快速进入药物研发管线。
COOH-MSNs Microspheres 的独特优势
高装载能力:规则的介孔结构和超大比表面积,确保小分子药物、核酸分子或蛋白质的高效负载;
表面可编程化学:羧基修饰为偶联抗体、肽段或靶向配体提供无限可能,实现个性化治疗方案;
可控药物释放:通过调控孔径大小与表面功能层,实现速释或缓释模式,延长药效并减少给药频率;
多功能平台:不仅可递送药物,还能结合影像对比剂,打造“诊疗一体化”解决方案。
中新康明的CDMO 服务内容
1. 处方开发与优化
精准筛选:药物-载体匹配策略(物理吸附/化学偶联/静电结合);
定制:靶向修饰(如叶酸、RGD肽、抗体);
构建:多药物协同递送体系,满足联合治疗需求。
2. 工艺与质量体系
工艺放大验证:从毫克级到百克级的平稳转化;
全面质量控制:包括粒径、Zeta 电位、药物包封率、释放曲线及稳定性研究;
CMC 文件支持:为 IND 申报和临床试验提供全套数据。
3. 功能化定制
诊疗一体化开发:药物+成像剂复合系统,提高临床可视化水平;
PEGylation 或智能聚合物修饰:延长循环时间、增强免疫逃逸能力;
抗体偶联:精准识别癌细胞,实现高度特异性治疗。
4. GMP 级生产与供应链
提供 GMP 车间条件下的规模化制备;
支持全球注册与监管合规;
提供长期稳定的临床前与临床阶段材料供应。
为满足不同研发阶段的需求,中新康明可提供中试放大及GMP级生产服务,支持从实验室研发到临床前或临床阶段的规模化生产。公司具备大批量生产能力,能够稳定供应高品质微球,帮助客户顺利推进医药研发和生产计划。
COOH-MSNs微球作为药物载体,其安全性和生物相容性是临床应用的基础。研究表明,COOH-MSNs在体内能够被有效地降解,且不会在体内积累,减少了长期使用可能带来的毒性风险。此外,COOH-MSNs的生物相容性良好,与生物体的相互作用较少,降低了免疫反应的发生。
在此过程中,中新康明可为客户提供定制化微球解决方案,无论是药物载体优化还是表面功能化改造,都能结合客户具体需求进行服务,确保产品符合医药研发的高标准要求。
参考文献引用COOH-MSNs微球
“Constructing Carboxylated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles to Deliver PD-L1 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Bladder Cancer”
中文摘要:
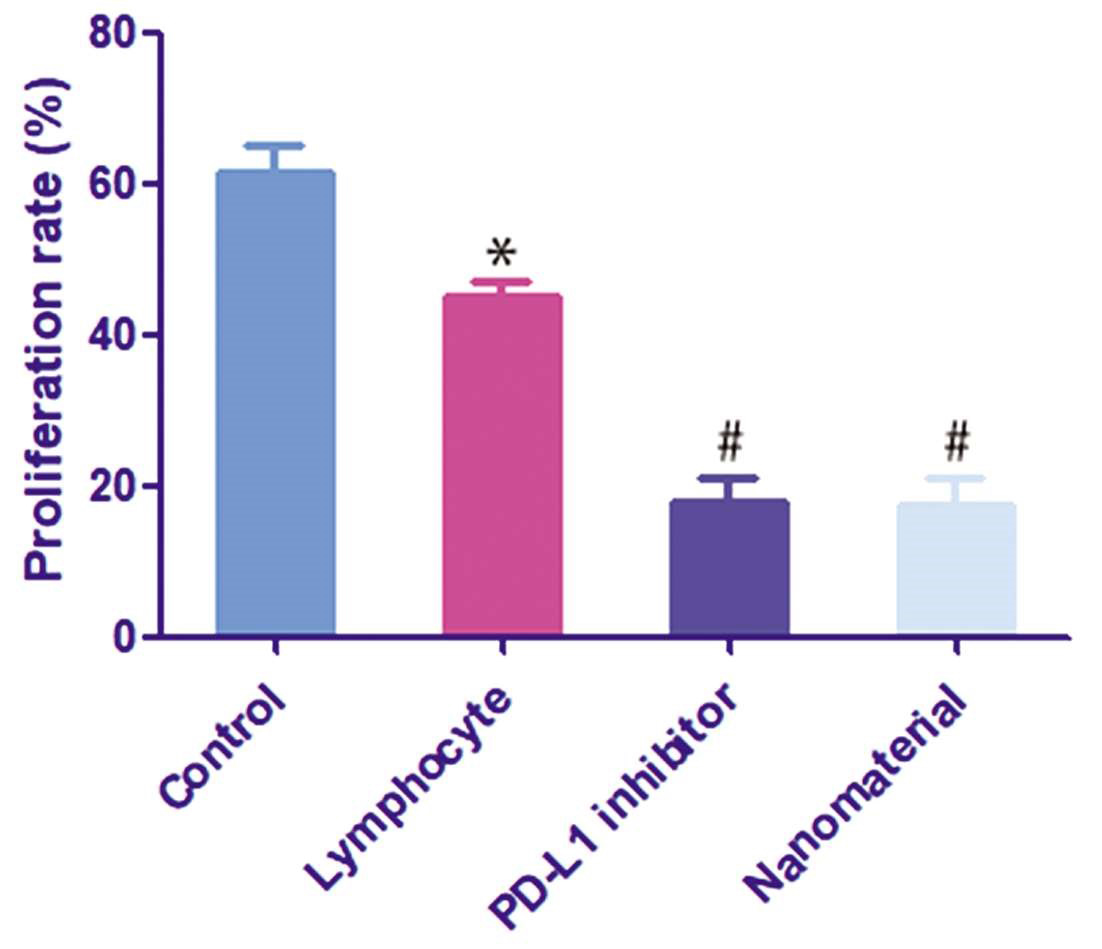
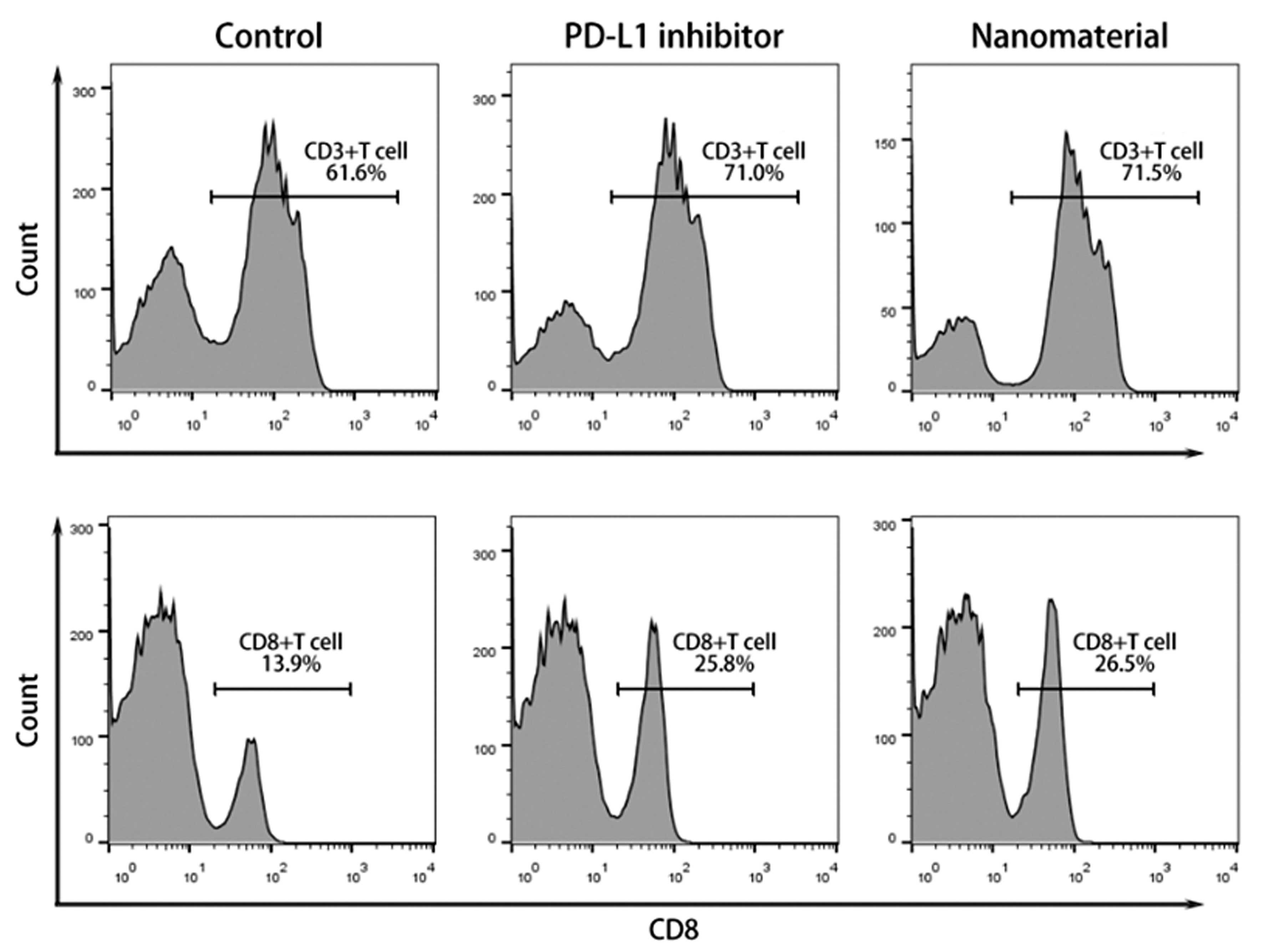
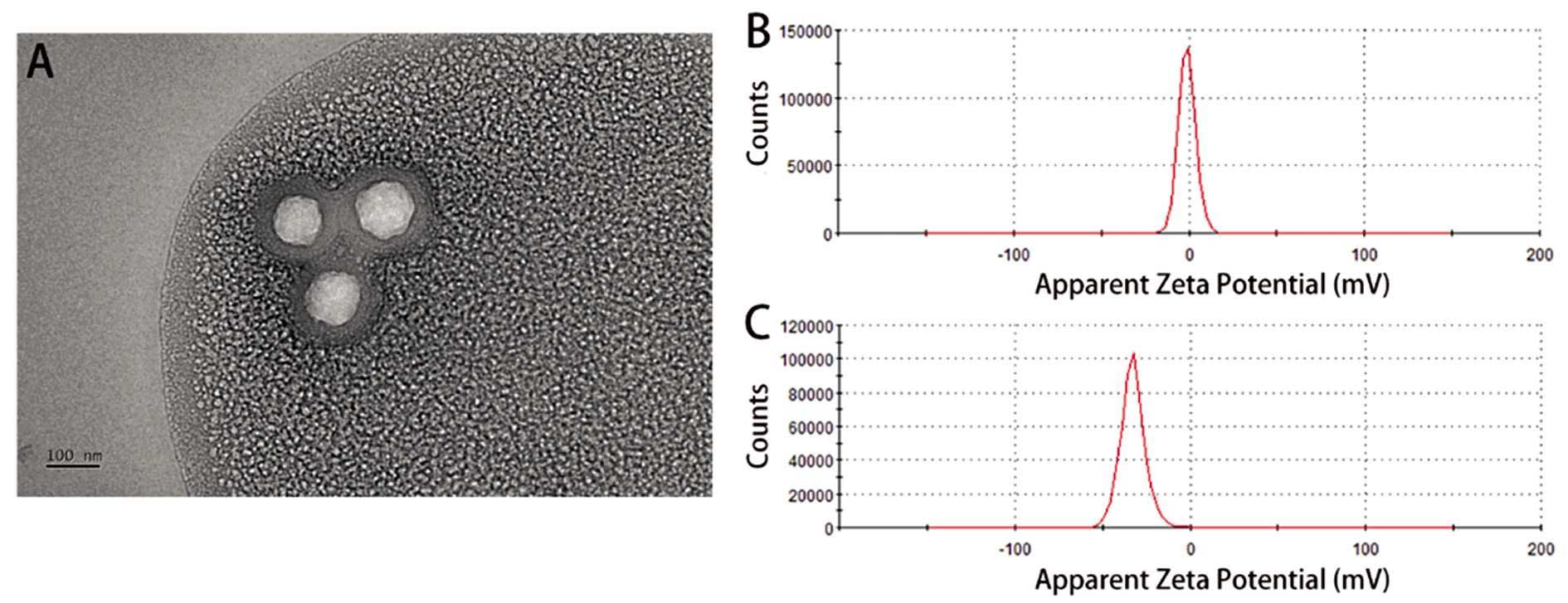
构建羧基化介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒(COOH-MSN)递送PD-L1抑制剂治疗膀胱癌。方法:构建负载PD-L1抑制剂的COOH-MSNs,透射电镜检测纳米颗粒的特征,zeta电位分析仪检测纳米颗粒的电位变化;流式细胞术检测血液中T细胞和CD8+T细胞的比例;MTT实验检测细胞增殖;构建小鼠荷瘤模型,HE染色检测基本的病理学变化,免疫组化检测ki-67的表达。结果:透射电镜结果显示纳米颗粒呈圆形,直径约为100 nm;COOH-MSNs表面带负电荷,BSA呈强负电性,BSA包封后纳米材料整体负电荷增强;纳米材料可显著提高T细胞和CD8+T细胞的比例,并进一步抑制膀胱癌细胞的增殖;动物实验结果显示纳米材料可抑制移植瘤的生长,且移植瘤内淋巴细胞的数量显著升高;免疫组化结果显示相对于PD-L1抑制剂组,纳米材料组ki-67增殖指数显著减低;HE染色结果显示PD-L1抑制剂组肾组织内可观察到血管充血、扩张和较多炎细胞浸润,而纳米材料组肾组织损伤程度显著降低。结论:我们构建了一种负载有PD-L1抑制剂的COOH-MSNs,可有效激活抗肿瘤免疫反应,并降低对正常器官的损伤。
英文摘要:
To construct carboxylated mesoporous silica nanoparticles (COOH-MSN) to deliver PD-L1 inhibitors for the treatment of bladder cancer. Methods: COOH-MSNs loaded with PD-L1 inhibitor were constructed, the characteristics of nanoparticles were detected by transmission electron microscopy, and the potential changes of nanoparticles were detected by zeta potential analyzer. Flow cytometry was used to measure the proportion of T cells and CD8+T cells in the blood. Cell proliferation was detected by MTT assay. The mouse tumor-bearing model was constructed, the basic pathological changes were detected by HE staining, and the expression of ki-67 was detected by immunohistochemistry. Results: The results of transmission electron microscopy showed that the nanoparticles were round and the diameter was about 100 nm. The surface of COOH-MSNs was negatively charged, the BSA was strongly electronegative, and the overall negative charge of the nanomaterial was enhanced after the BSA encapsulation. The nanomaterials significantly increased the ratio of T cells and CD8+T cells, and further inhibited the proliferation of bladder cancer cells. The results of animal experiments showed that the nanomaterials inhibited the growth of transplanted tumors and the number of lymphocytes in transplanted tumors increased significantly. The results of immunohistochemistry showed that the ki-67 proliferation index decreased significantly in the nanomaterial group compared with the PD-L1 inhibitor group. HE staining showed that vascular congestion, dilatation, and more inflammatory cell infiltration were observed in the renal tissue of the PD-L1 inhibitor group, while the degree of renal tissue injury was significantly reduced in the nanomaterial group. Conclusion: We constructed a COOH-MSN loaded with PD-L1 inhibitors, which can effectively activate anti-tumor immune response and reduce damage to normal organs.
 返回
返回